TLS
as you might have understand, otoroshi can store TLS certificates and use them dynamically. It means that once a certificate is imported or created in otoroshi, you can immediately use it to serve http request over TLS, to call https backends that requires mTLS or that do not have certicates signed by a globally knowned authority.
TLS termination
any certficate added to otoroshi with a valid CN and SANs can be used in the following seconds to serve https requests. If you do not provide a private key with a certificate chain, the certificate will only be trusted like a CA. If you want to perform mTLS calls on you otoroshi instance, do not forget to enabled it (it is disabled by default for performance reasons as the TLS handshake is bigger with mTLS enabled)
otoroshi.ssl.fromOutside.clientAuth=None|Want|Need
or using env. variables
SSL_OUTSIDE_CLIENT_AUTH=None|Want|Need
TLS termination configuration
You can configure TLS termination statically using config. file or env. variables. Everything is available at otoroshi.tls
otoroshi {
tls {
# the cipher suites used by otoroshi TLS termination
cipherSuitesJDK11 = ["TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_EMPTY_RENEGOTIATION_INFO_SCSV"]
cipherSuitesJDK8 = ["TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "SSL_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "TLS_ECDH_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "SSL_DHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "SSL_DHE_DSS_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA", "TLS_EMPTY_RENEGOTIATION_INFO_SCSV"]
cipherSuites = []
# the protocols used by otoroshi TLS termination
protocolsJDK11 = ["TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2", "TLSv1.1", "TLSv1"]
protocolsJDK8 = ["SSLv2Hello", "TLSv1", "TLSv1.1", "TLSv1.2"]
protocols = []
# the JDK cacert access
cacert {
path = "$JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts"
password = "changeit"
}
# the mtls mode
fromOutside {
clientAuth = "None"
clientAuth = ${?SSL_OUTSIDE_CLIENT_AUTH}
}
# the default trust mode
trust {
all = false
all = ${?OTOROSHI_SSL_TRUST_ALL}
}
# some initial cacert access, useful to include non standard CA when starting (file paths)
initialCacert = ${?CLUSTER_WORKER_INITIAL_CACERT}
initialCacert = ${?INITIAL_CACERT}
initialCert = ${?CLUSTER_WORKER_INITIAL_CERT}
initialCert = ${?INITIAL_CERT}
initialCertKey = ${?CLUSTER_WORKER_INITIAL_CERT_KEY}
initialCertKey = ${?INITIAL_CERT_KEY}
# initialCerts = []
}
}
TLS termination settings
It is possible to adjust the behavior of the TLS termination from the danger zone at the Tls Settings section. Here you can either define that a non-matching SNI call will use a random TLS certtificate to reply or will use a default domain (the TLS certificate associated to this domain) to reply. Here you can also choose if you want to trust all the CAs trusted by your JDK when performing TLS calls Trust JDK CAs (client) or when receiving mTLS calls Trust JDK CAs (server). If you disable the later, it is possible to select the list of CAs presented to the client during mTLS handshake.
Certificates auto generation
it is also possible to generate non-existing certificate on the fly without losing the request. If you are interested by this feature, you can enable it in the danger zone at the Auto Generate Certificates section. Here you’ll have to enable it and select the CA that will generate the certificate. Of course, the client will have to trust the selected CA. You can also add filters to choose which domain are allowed to generate certificates or not. The Reply Nicely flag is used to reply a nice error message (ie. human readable) telling that it’s not possible to have an auto certficate for the current domain.
Backends TLS and mTLS calls
For any call to a backend, it is possible to customize the TLS behavior
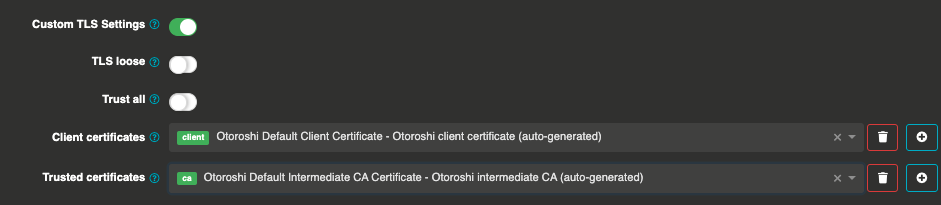
here you can define your level of trust (trust all, loose verification) or even select on or more CAs you will trust for the following backend calls. You can also select the client certificate that will be used for the following backend calls
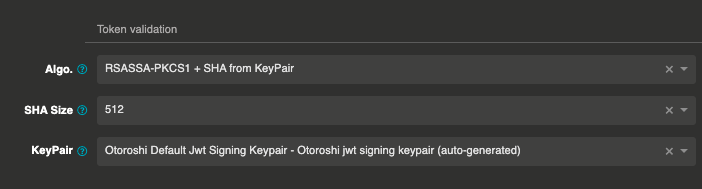
Keypair for signing and verification
It is also possible to use the keypair contained in a certificate to sign and verificate JWT token signature. You can mark an existing certificate in otoroshi as a keypair using the keypair on the certificate page.