Cluster mode

Izanami can be started in different cluster modes.
These modes impact behaviour of Izanami and which endpoints will respond.
What is cluster mode
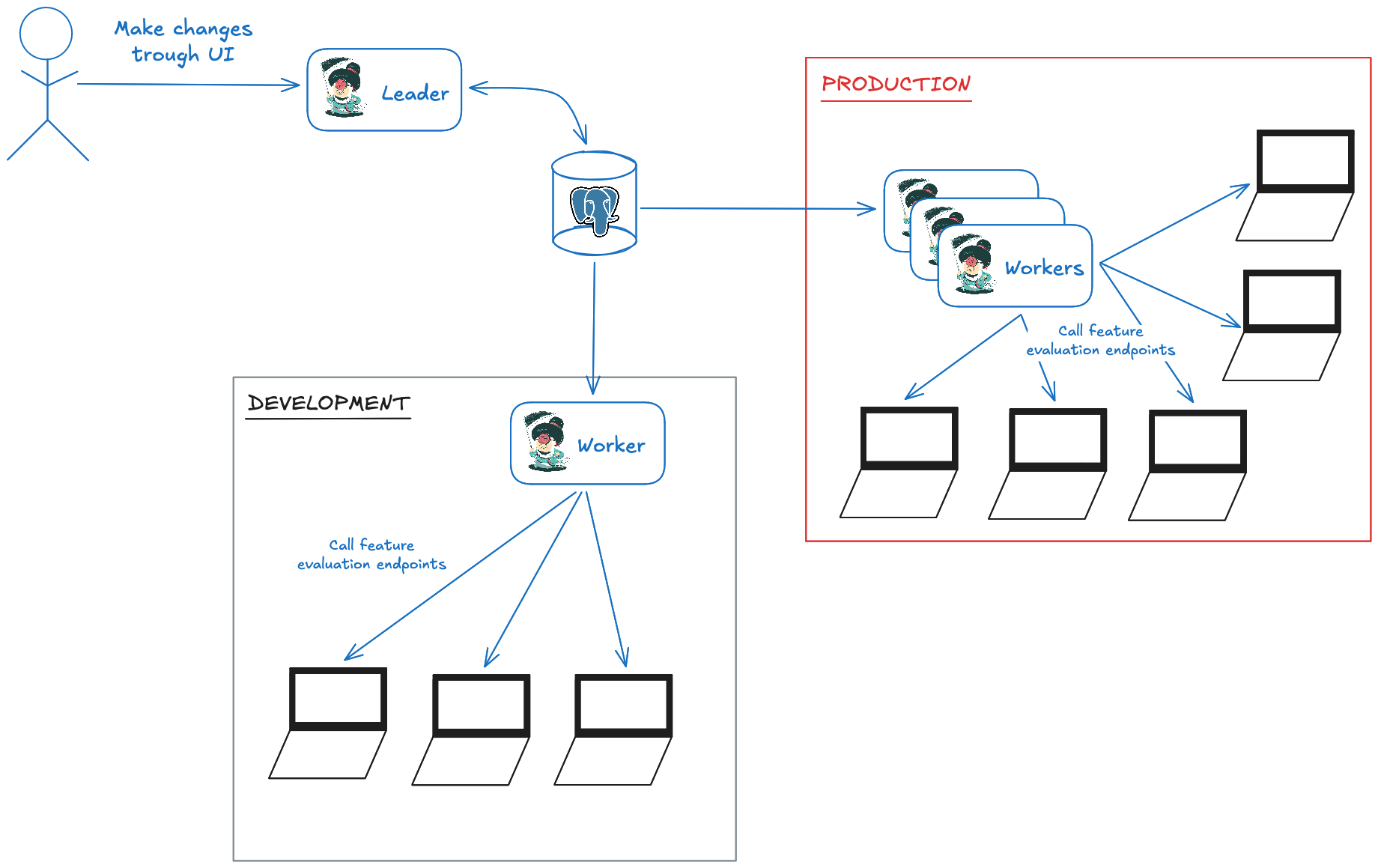
Cluster mode allows to separate two Izanami usages:
- UI access to create / update / delete entities (feature, projects, tenants, ...)
- Client access to evaluate feature state
Leader / worker modes allow separating these concerns to prevent UI from being impacted by spikes of client queries.

Scaling worker will help handling spikes of requests, however keep in mind that both leader and worker nodes use the same underlying database. At some point you may want to scale database as well.
Setting cluster mode
Cluster mode can be set using either:
app.cluster.modeJAVA commande line argumentIZANAMI_CLUSTER_MODEenvironnement variable
Possible values are standlone, worker and leader, default value is standalone.
Worker mode
Instantiating Izanami in worker mode will:
- Allow it to respond to feature evaluation requests
- prevent it from serving UI and associated admin endpoints (including call using Personnal Access Tokens).
Leader mode
Instantiating Izanami in leader mode will:
- Prevent it from responding to feature evaluation requests
- Allow it to serve UI and associated admin endpoints (including call using Personnal Access Tokens).
Standalone mode
standalone mode is the default mode. When an instance is started in standalong mode, it will serve both the UI (and associated admin endpoints) and client endpoints.
Mode summary
| Expose UI | Expose admin endpoints (through Personnal Access Tokens) | Expose client (feature evaluation) endpoints | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worker | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Leader | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Standalone | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Instanciation example
Worker specialization
In order to prevent accidental calls from one environnement to another, Izanami allows defining blocklist and allowlist on worker instances.
Read dedicated configuration section to learn more about these blocklists and allowlists.