Scripts
With Izanami, scripts can be evaluated to decide if a feature is active or not. You have the choice between 3 languages :
- javascript
- scala
- kotlin
When writing a script, you have access to
context: A json object send by the clientenabled: A function to call, the feature is enableddisabled: A function to call, the feature is disabledhttp: An http client that can be used to request an API.
Debugging
You can debug script in the UI
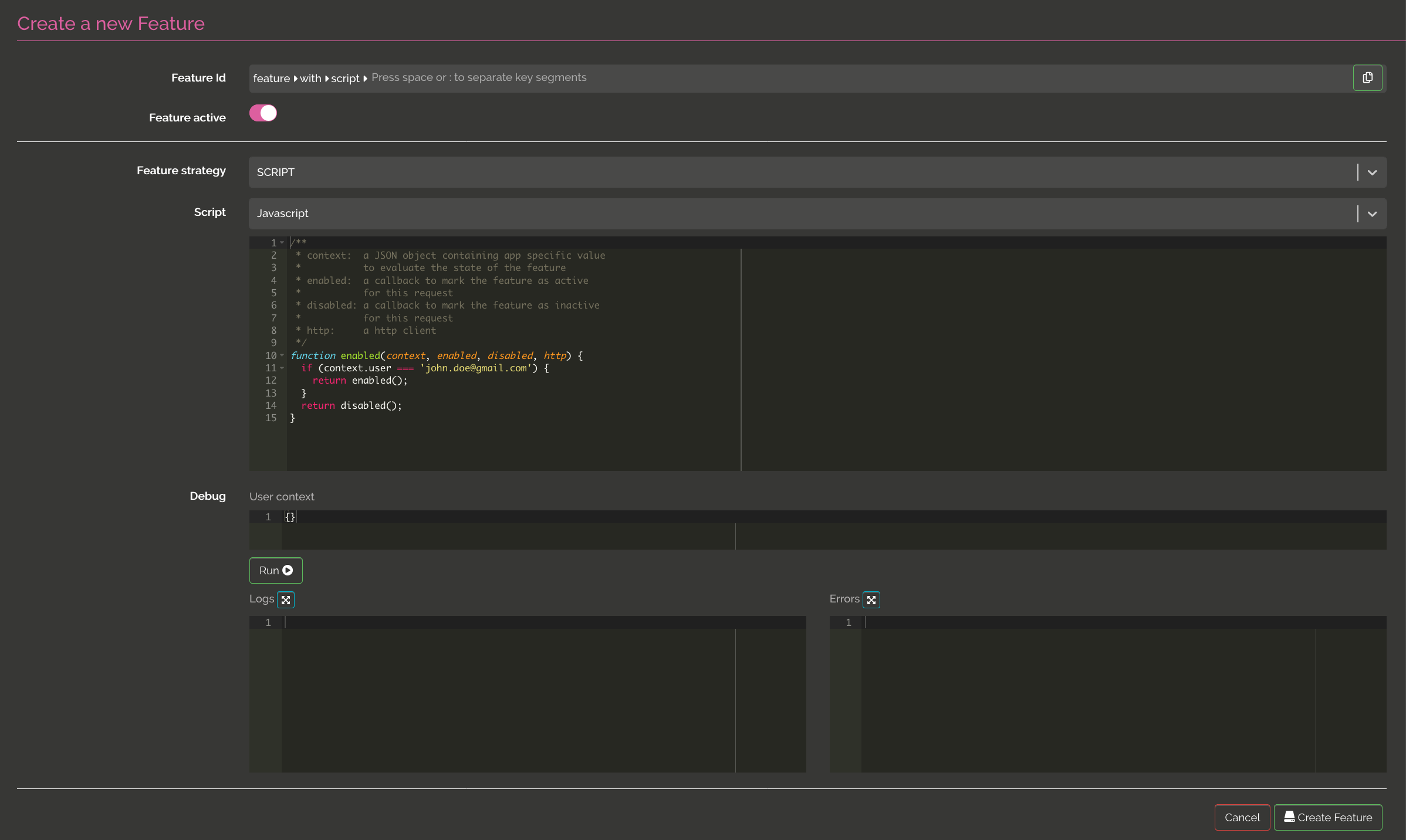
Click on the run button to test the script, compiling errors will be printed on the right panel.
You can print logs using println in scala or kotlin and console.log in javascript.
The logs will be printed on the left panel.
Writing script with javascript
The http client expose the call method that take two args :
options, an object with the following possible attributesurl(required): The url to call.method(default get): The http method betweenget,post,put,delete,option,patchheaders: A object with headerName -> Valuebody: An optional json string
callback: A bifunction with failure or success.
function enabled(context, enabled, disabled, http) {
http.call(
{
url: "http://localhost:9000/api/features/feature:with:script/check",
method: "post",
headers: {
"Izanami-Client-Id": "xxxx",
"Izanami-Client-Secret": "xxxx",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
user: context.user,
}),
},
function (error, success) {
if (error) {
return enabled();
} else {
var resp = JSON.parse(success);
if (resp.active) {
return enabled();
} else {
return disabled();
}
}
}
);
}
Writing script with scala
In scala, the http client is the default playframework WSClient and the json value is play json JsValue. You can find more information here :
- http client: https://www.playframework.com/documentation/2.6.x/ScalaWS
- json : https://www.playframework.com/documentation/2.6.x/ScalaJson
A example script doing an http call could be
def enabled(context: play.api.libs.json.JsObject,
enabled: () => Unit,
disabled: () => Unit,
http: play.api.libs.ws.WSClient)(implicit ec: ExecutionContext): Unit = {
import scala.util._
http.url("http://localhost:9000/api/features/you:can:write:script:with:scala/check")
.addHttpHeaders(
"Izanami-Client-Id" -> "xxxx",
"Izanami-Client-Secret" -> "xxxx"
)
.post(context)
.onComplete {
case Success(response) =>
response.status match {
case 200 if (response.json \ "active").asOpt[Boolean].contains(true) =>
enabled()
case other =>
println(s"Oups $other")
disabled()
}
case Failure(e) =>
println(s"Oups $e")
disabled()
}
}
Writing script with kotlin
In kotlin, the http client is the default playframework java WSClient and the json value is jackson JsonValue. You can find more information here :
- http client: https://www.playframework.com/documentation/2.6.x/ScalaWS
- json : https://www.playframework.com/documentation/2.6.x/ScalaJson
A example script doing an http call could be
fun enabled(context: JsonNode, enabled: () -> Unit, disabled: () -> Unit, wsClient: WSClient) {
wsClient.url("http://localhost:9000/api/features/you:can:write:script:with:kotlin/check")
.addHeader("Izanami-Client-Id", "xxxx")
.addHeader("Izanami-Client-Secret", "xxxx")
.post(context)
.whenComplete { wsResponse, e ->
if (e != null) {
disabled()
} else {
when (wsResponse.getStatus()) {
200 -> {
val jsonBody = wsResponse.asJson()
if(jsonBody.get("active")?.asBoolean() ?: false) {
enabled()
} else {
println("oups: ${jsonBody}")
disabled()
}
}
else -> {
println("oups: ${wsResponse.getStatus()} ${wsResponse.getBody()}")
disabled()
}
}
}
}
}